|
What's in the Water Makes a Difference
JACK GREER
|
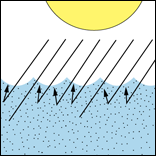
Sediment scatters light...
|
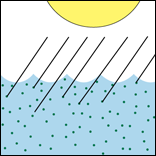
...Algae absorbs it
|
LIGHT HEADING FOR THE BOTTOM of the Bay gets lost in two ways, not counting shading. It gets scattered or it gets absorbed.
Scattering. When light hits water filled with fine inorganic sediment, it bounces around (see figure below left). Some light will eventually get to the bottom, though greatly reduced or "attenuated."
Absorption. When light hits an algae cell, much of it gets absorbed (see figure above right). Phytoplankton are great absorbers of light — in a very real way, they "feed" on light. Larry Sanford and Charles Gallegos are reaching between their disciplines to discover the ways in which the inorganic and organic interact to create the turbidity we now see in the Chesapeake Bay. To learn more about light and turbidity, see Related Links. |
 |
 |
|
The image on the left, captured on video by researcher Larry Sanford, shows fine grains of sediment and flocculants — aggregations made up of many thousands of smaller particles. The image on the right, of the diatom
Asterionella glacialis, is one of dozens of phytoplankton species found in the Bay. Diatom image by Sharyn Hedrick, courtesy of the SERC Phytoplankton Lab. |
|

